Military Application of Infrared Thermal Imaging

Compared with the radar system, the infrared thermal imaging system has higher resolution, better concealment, and is less susceptible to electronic interference. Compared with the visible light system, it has the advantages of being able to identify camouflage, work day and night, and less affected by weather. Therefore, it is widely used in the military. Its main applications are:
Infrared night vision
The infrared night vision devices used in the early 1950s are all active infrared night vision devices, which generally use infrared image changer tubes as receivers, and the working band is about 1 micron. Tanks, vehicles and ships 10 km away.
Modern infrared night vision equipment mainly includes infrared thermal camera (also known as infrared forward vision systems), infrared TVs and improved active infrared night vision devices. Among them, the infrared thermal imager is a representative infrared night vision device.
An optical-mechanical scanning infrared imaging system developed by the United States in the late 1960s provides observation means for aircraft flying at night and flying under severe weather conditions. It works in the 8-12 micron range and generally uses mercury cadmium telluride photon detectors to receive radiation, liquid nitrogen refrigeration. Its tactical and technical performance is an order of magnitude higher than that of active infrared night vision devices. At night, people at a distance of 1 kilometer can be observed, tanks and vehicles at a distance of 5 to 10 kilometers, and ships within visual range.
This kind of thermal camera has been improved several times. By the early 1980s, standardized and componentized systems had appeared in many countries. Designers can choose different components according to requirements and assemble the required thermal imaging cameras, provided a simple, convenient, economical and interchangeable night vision equipment for the army.
Infrared night vision equipment has been widely used in the land, sea and air forces. Such as observation equipment for night driving of tanks, vehicles, aircraft, ships, etc., night sights for light weapons, fire control systems for tactical missiles and artillery, frontier surveillance and observation equipment on the battlefield, and individual reconnaissance equipment. In the future, a thermal imaging system composed of a staring focal plane array will be developed, and its tactical and technical performance will be further improved.
Infrared guidance
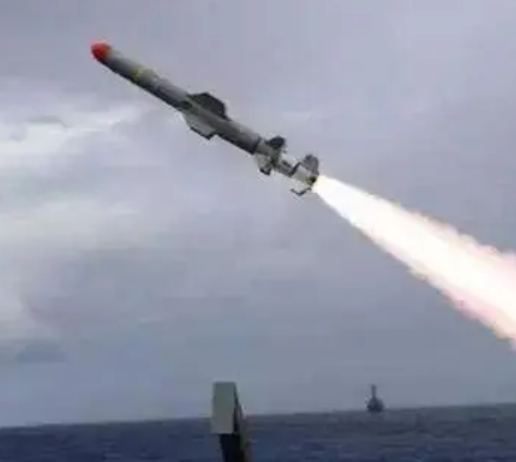
With the development of infrared technology, the infrared guidance system is becoming more and more perfect. After the 1960s, practical infrared systems have been available in the three atmospheric windows. The attack method has developed from tail pursuit to omnidirectional attack. The guidance method also has full infrared guidance (point source guidance and imaging guidance) and composite guidance (infrared guidance). /TV, infrared/radio command, infrared/radar infrared point source guidance system has been widely used in dozens of tactical missiles such as air-to-air, ground-to-air, shore-to-ship and ship-to-ship missiles.
Infrared reconnaissance
Infrared reconnaissance equipment for ground (water), air and space, including thermal camera, infrared scanners, infrared telescopes and active infrared imaging systems, etc. Ground infrared reconnaissance equipment is mainly infrared thermal imager and active infrared night vision device.
The infrared periscope used by submarines already has the function of protruding out of the water to quickly scan for a week, and then displaying the function of observing after retracting. Surface ships can use the infrared detection and tracking system to monitor the invasion of enemy aircraft and ships. In the early 1980s, most of them used point-source detection systems. The distance to detect aircraft head-on was 20 kilometers, and the distance to tail-track was about 100 kilometers; the distance to observe active strategic missiles was greater than 1,000 kilometers.
Infrared countermeasures
The application of infrared countermeasure technology can greatly reduce the function of the opponent’s infrared detection and identification system, or even make it ineffective. Countermeasures can be grouped into two categories: evasion and deception. Evasion is the use of camouflage equipment to conceal military facilities, weapons and equipment, so that the other party cannot detect its own infrared radiation source.
Post time: May-10-2023